How Inspection Companies in China Ensure Compliance with International Standards
How Inspection Companies in China Ensure Compliance with International Standards
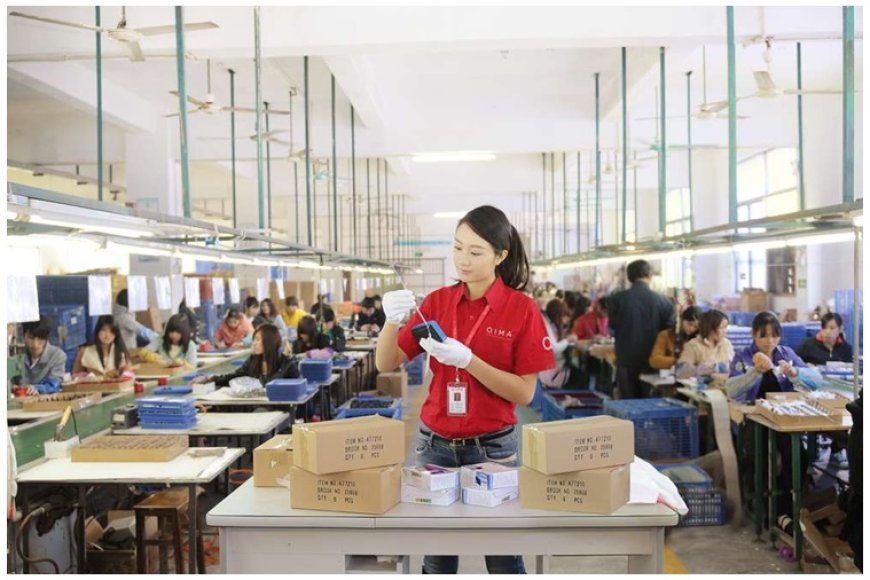

Ensuring products meet global standards is a big job. In China, where factories make many items sold around the world, inspection companies play a key role. They help factories follow rules set by groups like ISO, ASTM, and individual buyers. This blog will explain in simple words how inspectors check and make sure everything is right. Well look at why standards matter, what inspectors do, the tools they use, and why these checks help everyone.
Why International Standards Matter
International standards are like rules for making things safely and well. When products follow these rules, buyers trust them more. For example, ISO standards cover many topics, from safe foods to strong car parts. ASTM standards often help with material strength and safety tests. Some buyers even make their own rules, called customer-specific standards.
Following these standards helps everyone:
Factories know how to make good products.
Buyers get items that work right.
People stay safe because products are tested.
Trade between countries runs smoothly.
Role of inspection companies in China
So, what do inspection companies in China do? They visit factories, check products, and write reports. They act like the eyes and ears of international buyers. Factories make items, but inspectors make sure those items meet the rules before shipping.
Inspectors work in many industries: toys, electronics, clothes, and more. They help factories see problems early. This means fewer returns and happier customers. Think of inspectors like quality helpers who watch factories follow the instructions.
Understanding Key International Standards
There are many rules, but the most common are:
ISO Standards
ISO, or International Organization for Standardization, writes rules for safety and quality across many fields. For example:
? ISO 9001 is about managing quality
? ISO 14001 is about protecting the environment.
? ISO 22000 covers food safety.
Inspectors know these rules and check factories against them.
ASTM Standards
ASTM, the American group, sets material and testing standards. They test things like:
Plastic strength.
Metal hardness.
Textile durability.
Inspectors use ASTM tests to see if materials meet specs.
Customer-Specific Standards
Some buyers have special needs. A toy company may ask for extra safety tests. A tech firm might demand stricter electronic checks. Inspectors follow these custom rules just as carefully as ISO or ASTM.
Steps Inspectors Take to Verify Compliance
Inspectors follow clear steps. Heres how they do it:
1. Document Review
Before going to the factory, inspectors look at paperwork. They check:
? Production plans.
? Material certificates.
? Testing records.
This helps them know what to expect and what rules to follow.
2. Factory Audit
Inspectors visit the factory to see how work flows. They look at:
? Facility layout.
? Equipment status.
? Staff training.
This audit shows if the factory can keep doing Quality control services correctly day after day.
3. Sampling Products
Inspectors dont check every item. They use sampling plans:
? Randomly pick items.
? Follow the buyer's sample size.
? Test these samples for problems.
Sampling helps balance speed and accuracy.
4. Testing and Measurement
Once samples are chosen, inspectors test them. Tests include:
? Measuring size with calipers.
? Checking material with lab tools.
? Running stress or safety tests.
They follow ISO, ASTM, or customer rules step by step.
5. Visual Inspection
Some checks need only eyes:
? Look for scratches or dents.
? Check color and finish.
? Verify labels and packaging.
This step catches visible flaws.
Tools and Techniques Used by Inspectors
Inspectors use many tools to make sure tests are right. These tools include:
? Calipers and micrometers for exact measurements.
? Hardness testers for metals and plastics.
? Spectrometers for checking chemical makeup.
? Electrical testers for electronics.
? pH meters for food or chemical products.
Besides tools, inspectors also use software. They log data, make charts, and share reports fast. This digital way helps buyers see results quickly.
Reporting and Documentation
After checking, inspectors write detailed reports. Reports have:
1. Summary of findings.
2. Photos of any problems.
3. Test data and measurements.
4. Pass/fail results for each rule.
5. Recommendations for fixes.
Buyers read these reports to decide if they accept or reject products. Sometimes factories get corrective action plans, which are steps to fix issues. Inspectors may come back to check if the fixes work.
Challenges and Solutions
Inspection is not always easy. Here are some challenges:
? Language barriers: Inspectors and factory staff may speak different languages. Solution: Use translators or bilingual inspectors.
? High volume: Factories can make thousands of items each day. Solution: Strict sampling plans focus on highest risk areas.
? Custom rules: Every buyers rules can differ. Solution: Inspectors maintain up-to-date checklists for each buyer.
? Remote locations: Some factories are far away. Solution: Mobile labs and local inspector teams help reach these sites.
By facing these challenges head-on, inspectors keep Quality control services reliable and fast.
Benefits to Customers and Factories
Good inspections help both sides:
? Customers get safe, high-quality products without surprises.
? Factories learn how to improve processes and reduce waste.
? Buyers build trust in their brand when products arrive as promised.
? Markets benefit because trade runs smoothly with clear rules.
In the long run, this teamwork leads to better products and happier customers around the world.
How Technology is Shaping Inspections
As technology grows, inspection methods improve:
? Drones can scan large warehouse shelves or factory floors.
? AI and Machine Learning help spot patterns in defects and predict future issues.
? Mobile apps allow real-time data entry and instant report sharing.
? Blockchain can secure records, making data tamper-proof.
These tools make inspections faster, safer, and more reliable. They also help inspectors focus on tricky tasks instead of routine checks.
Tips for Factories to Stay Compliant
Factories can do a few things to make inspections smoother:
1. Train staff on standards and testing methods.
2. Keep records organized and up-to-date.
3. Maintain equipment regularly to ensure accurate results.
4. Use control charts to track product quality over time.
5. Communicate clearly with inspectors and buyers about requirements.
By following these tips, factories can reduce rejections and save time and money.
Conclusion
Inspection work is vital to ensure products meet rules from ISO, ASTM, or specific buyers. In China, inspection companies provide essential Quality control services that help factories and customers. They review documents, audit factories, sample products, run tests, and report clearly. With new technology and strong teamwork, inspectors help keep global trade fair, safe, and efficient. Next time you buy something made in China, remember that a team of inspectors worked hard to make sure it met the highest standards.